What Is Physical Therapy?
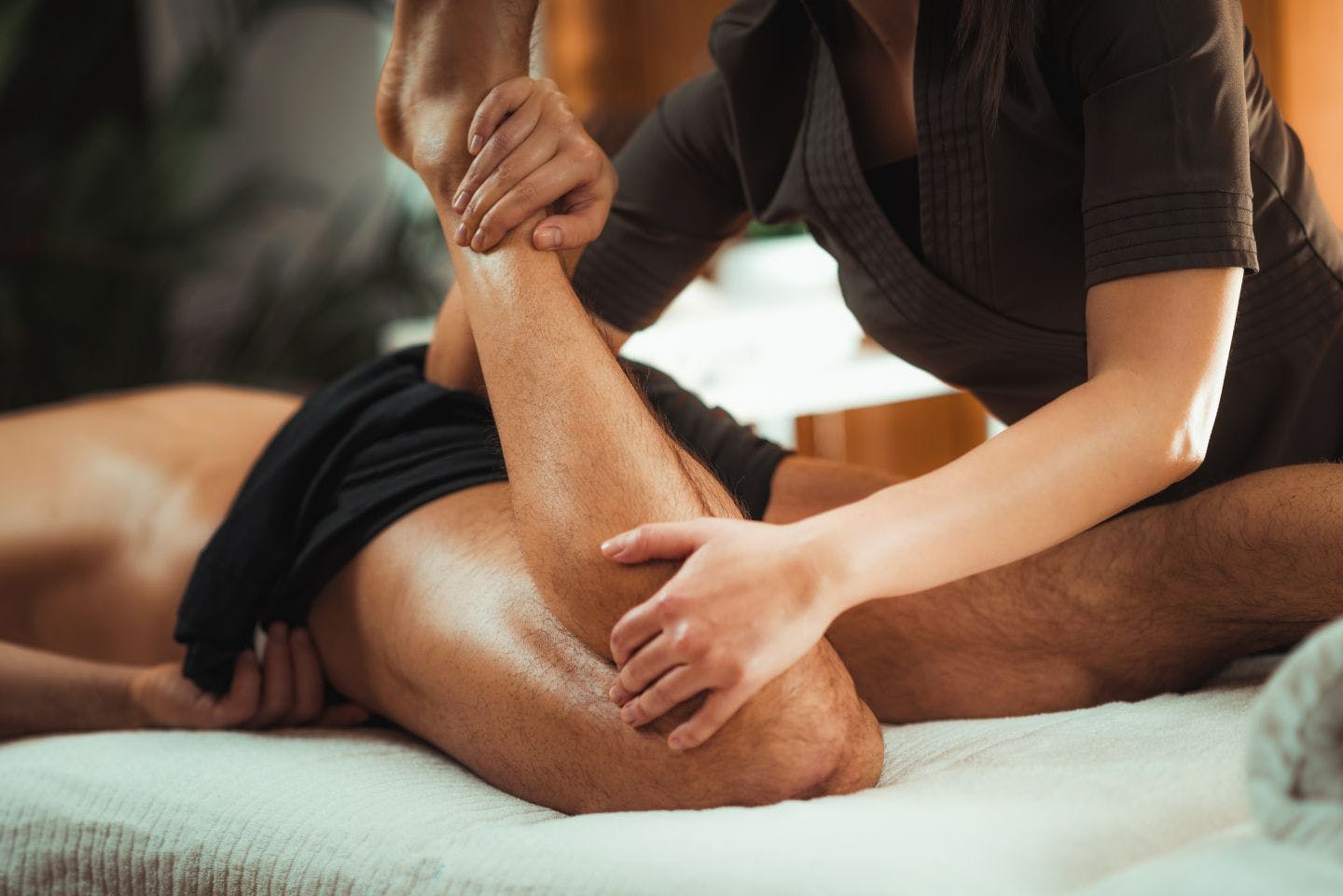


Physical therapy (often referred to as PT) is the health care specialty primarily concerned with individualized treatment:
- For patients who may need to recover from injuries,
- For post-surgical rehabilitation or
- To help patients cope with health problems that make it difficult to move around and perform everyday tasks.
Physical therapy treatment promotes healing and helps to manage or relieve pain. Physical therapy also aims to restore and improve the physical function and fitness level of the patient. Often doctors or surgeons recommend physical therapy treatment following a surgery or injury, or for management of chronic health problems such as arthritis or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). Physical therapy may be used alone or with other medical treatments.
- Promote mobility
- Reduce pain
- Restore function
- Prevent disability
- Increase strength
- Promote healing
- Improve quality of life
- Post-surgical recovery
- Age-related issues
- Management of chronic conditions
- Car accident injuries
- Workers comp rehabilitation
- Athletic performance
Sports-Focused Physical Therapy is a more specialized type of physical therapy treatment athletes turn to for recovery from physical injuries (sometimes following a subsequent surgery) and prevention of future injury.
Methods of Physical Therapy Treatment
Exercise
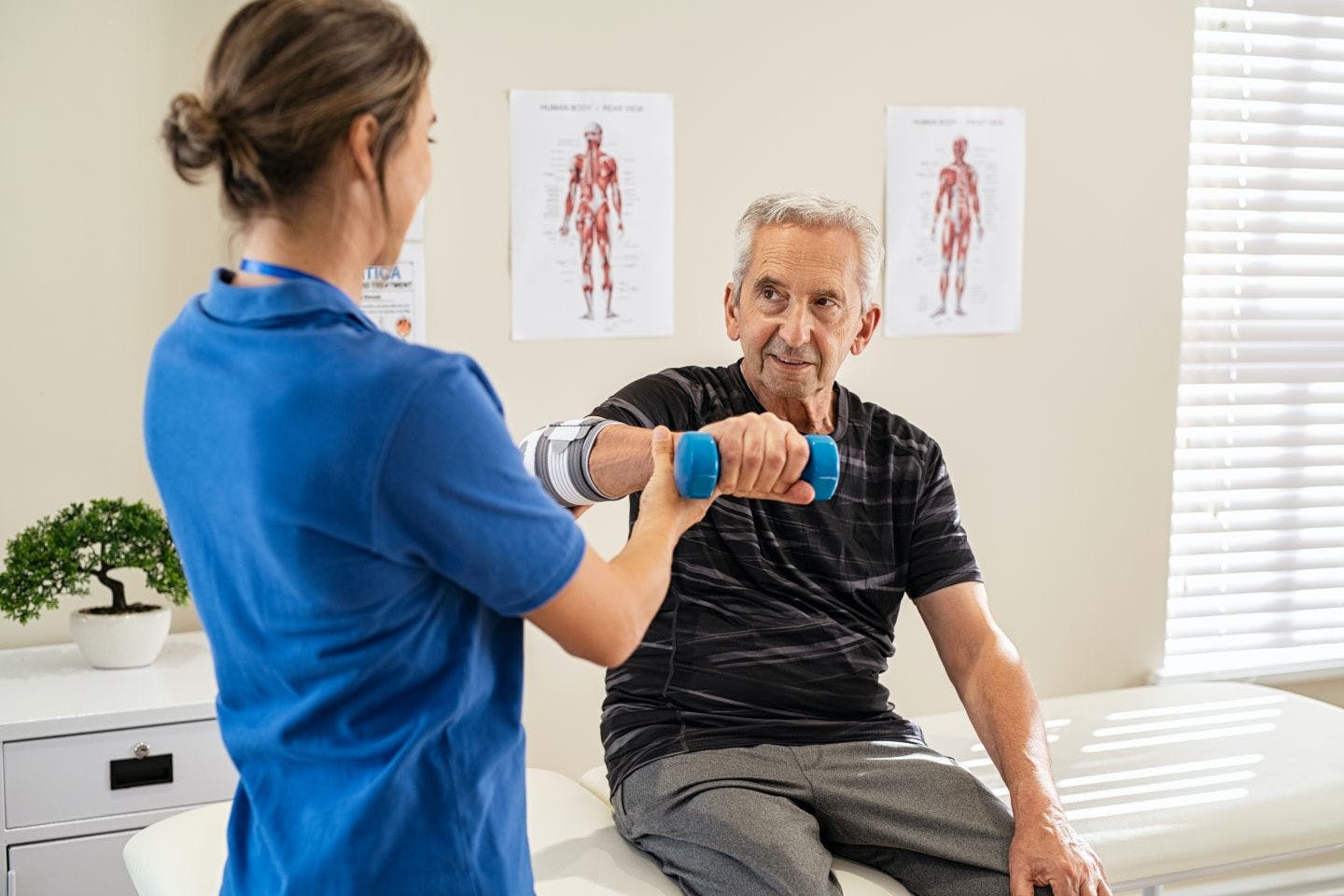

Physical therapy nearly always involves exercise of some kind that is specifically designed for the patient’s injury, illness, condition, or to help prevent future health problems. It can include stretching, core exercises, weight lifting, and walking.
Manual Therapy
Manual therapy (sometimes called bodywork) is a general term for physical therapy treatment performed mostly by a physical therapist with the hands. The goals of manual therapy include relaxation, decreased pain, and increased flexibility. Types of manual therapy can include:
- Massage. Pressure is applied to the soft tissues of the body, such as the muscles. Massage can help relax muscles, increase circulation, and ease pain in the soft tissues.
- Mobilization. Slow, measured movements are used to twist, pull, or push bones and joints into position. This can help loosen tight tissues around a joint and help with flexibility, range of motion and alignment.
- Manipulation. Pressure is applied to a joint. It can be done with the hands or a special device. The careful, controlled force used on the joint can range from gentle to strong and from slow to rapid.
Other treatment methods include:
Cold and Ice
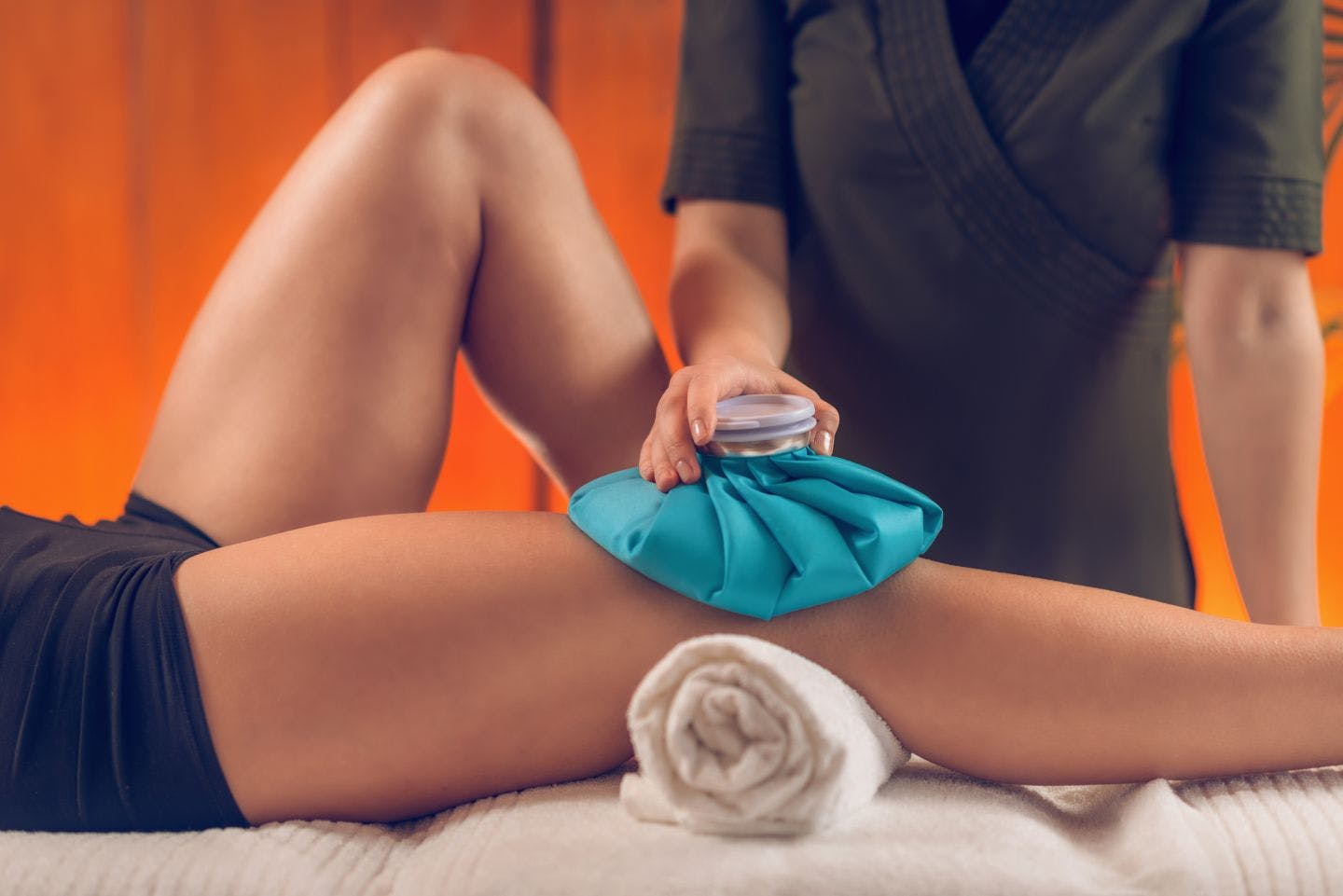


To relieve pain, swelling, and inflammation from injuries and other conditions such as arthritis. Ice can be used for up to 20 minutes at a time. In some cases, ice may be used several times a day. Some therapists also use cooling lotions or sprays.
Heat
To help relax and heal your muscles and soft tissues by increasing blood circulation. This can be especially helpful if a joint is stiff from osteoarthritis or from being immobilized. Heat can also relax the muscles before exercise.
Ultrasound
Uses high-pitched sound waves to ease muscle spasms and relax and warm muscles before exercise, to help relieve pain and inflammation, and to promote healing.
Electrical Stimulation
In general, this is the use of electrical current to create an effect in the body. Electrical stimulation is sometimes used at low levels to reduce the feeling of pain. It can also be used to cause muscles to contract (tense).
Hydrotherapy
Also known as water therapy, a term from the past that means the use of water to treat a disease or to maintain health. The most common hydrotherapy now is water exercise.
Dry Needling
Dry Needling is also known as intramuscular stimulation (IMS) and trigger point dry needling (TDN). It is a safe, effective and efficient treatment used to:
- Relax myofascial trigger points, and
- Restore normal muscle tones, muscle length, coordination, function and strength
Dry needling involves insertion and repetitive manipulation of a “dry”, solid filament needle in a trigger point in order to produce an involuntary spinal cord reflex, also known as a local twitch response (LTR). This results in lasting muscle relaxation due to the release of shortened bands of muscle fibers for overactive (tight) muscles or the activation of under-active (weak) muscles. Deactivation of the trigger points can bring immediate relief of symptoms, so the therapist can immediately train the muscles to work with the newly gained pain free range of motion (ROM).
Conditions Treated by Dry Needling
Dry needling has successfully been used to treat a variety of conditions including:
- Head and Neck Pain – including whiplash and headaches / migraines, degenerative joint disease, degenerative disk disease or osteoarthritis
- Otological (Ear) and Opthamological (Eye) Pain – including tinnitus and eye strain
- Dental (Teeth) and Orthodontic (Jaw and Occlusal) Pain – including cavities, temporomandibular joint (TMJ) dysfunction, tooth impaction and root problems
- Shoulder Pain – including rotator cuff muscle tears, bursitis, adhesive capsulitis (frozen shoulder), tendonitis and impingement syndrome
- Elbow Pain – including lateral epicondylitis (tennis elbow) and medial epicondylitis (golfer’s elbow)
- Hand and Wrist Pain – including gamekeeper’s thumb, DeQuervain’s syndrome, carpal tunnel syndrome, degenerative joint disease and osteoarthritis
- Back and Hip Pain – including lumbar degenerative disc disease, arthritic changes and herniated discs
- Knee Pain – including degenerative joint disease or osteoarthritis
- Shin / Ankle / Foot Pain – including shin splints, gout, metatarsalgia and Morton’s neuroma
- Plantar Fasciitis (Heel Pain)
- Acute and Chronic Tendonitis
- Athletic and Sports-related Overuse Injuries
- Post-surgical Pain
- Post-traumatic Injuries, Motor Vehicle Accidents (MVA), and Work-related Injuries
- Other Chronic Pain Conditions – including myofascial pain and myofascial pain syndrome (MPS)
Dry Needling vs. Acupuncture
Dry needling is similar to acupuncture in the sense that a dry, solid filament needle is inserted and manipulated under the skin to release endorphins and serum cortisol for pain relief. The difference is that dry needling is based on western neuroanatomy and modern scientific study of the musculoskeletal and nervous systems. Acupuncture is based on traditional Chinese medicine (TCM). It creates balance in the body by influencing the flow of Qi (energy) in pathways called meridians to achieve pain relief and alleviate inflammation.
Physical Therapy Importance


With customized physical therapy treatment, it is possible for a patient to regain the mobility of his/her joints, gain flexibility, and acquire improved balance and coordination. In addition, physical therapy also helps in significantly improving the overall fitness and health of the patient.
Physical therapy can help a patient recover from an injury and avoid future injury. Physical therapy can help patients reduce pain in the soft tissues (muscles, tendons, and ligaments), build muscle strength and function, improve flexibility and function and joint range of motion. Physical therapists also evaluate how patients perform an activity and make suggestions for doing the activity in a way that is less likely to result in an injury.
Additionally, there are also more specific reasons why one might choose physical therapy. Athletes who are looking to enhance their athletic performance and lessen the occurrence of injuries may use physical therapy to achieve their goals. Read more about Sports-Focused Physical Therapy here.
Overall, the importance of physical therapy is based on the individual needs and lifestyle of each patient. Besides the more obvious reasons related to pain, and increased mobility, physical therapy may also be important for helping a patient function within the limitations of a chronic or debilitating condition.
